Fueling the Body Right Battling Lack of Nutrients, lack of nutrients, also known as malnutrition or nutritional deficiency, occurs when your diet doesn't provide enough essential calories, protein, vitamins, and minerals your body needs for proper function. This can lead to various symptoms like fatigue,weight loss and muscle, a weakened immune system, slow wound healing, and cognitive impairment. Treatment involves a balanced diet to intake of necessary macronutrients and micronutrients.
Causes of Nutritional Deficiency:
- 1-Dietary Inadequacy:
Not eating enough of the right foods to meet your body to needs. - 2-Absorption Issues:
Conditions that prevent the body from properly absorbing nutrients, such as impaired absorption - 3-Underlying Health Conditions:
Chronic diseases, eating disorders or conditions that lead to an inability to eat. - 4-Environmental Factors:
Poverty, food insecurity, and natural disasters can contribute to malnutrition.
6 Sign of Nutrients Deficiency:
Some of nutrients deficiency are following:
1- Serve to hair loss
2-Burning sensation in the feet or tongue
3- Wounds are slow to heal
4- Bone pain
5-Irregular heartbeat
6-Your night vision deteriorates
Importance of Nutrients Deficiency:
Some important of nutrients deficiency are following:
- Long-Term Health:
Addressing deficiencies early in life can prevent lifelong complications and set the stage for better long term of health. - Improved Quality of Life:
Timely intervention helps individuals maintain their health, function and participate fully in work, education, and community life. - Preventing Vicious Cycles:
Malnutritional can worsen existing diseases and diseases can cause malnutrition. Addressing nutritional status helps break this cycle. - Reduced Healthcare Costs:
Early identification and intervention through nutritional assessment can improve healthcare outcomes, shorten recovery times and reduce hospital stays.
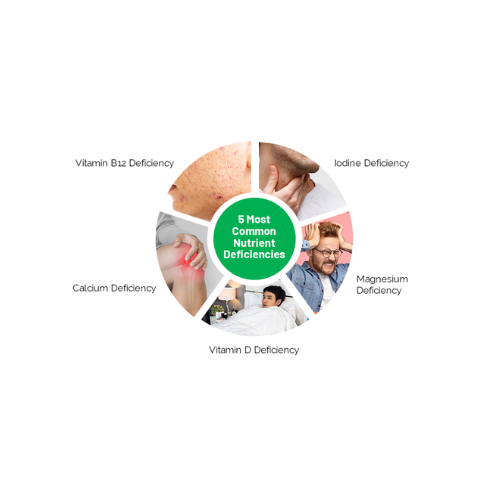
7 Common Nutrients Deficiency:
Some common nutrients deficiency are following:
1-Calcium:
Calcium is important for maintaining strong bones and controlling muscle and nerve function. Signs of severely low calcium include numbness, tingling fingers and abnormal heart rhythms. There are no short-term, obvious symptoms of calcium deficiency.
2- Vitamin D:
Vitamin D is also crucial for bone health. There is some evidence that low vitamin D levels in the blood are associated with increased risk of breast and prostate cancer, but it's not known if supplementing reverses this risk.
3- Potassium:
Potassium helps your heart, nerves, and muscles work properly and also delivers nutrients to cells while removing waste. It is an useful nutrient that also helps offset sodium's negative impact on your blood pressure.
4- Iron:
Iron is an essential mineral for the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin, which carry oxygen throughout the body.[11] When iron levels get too low, there may be a deficiency in red blood cells, resulting in a condition called iron deficiency anemia.
5- Vitamin B12:
Vitamin B12 aids the production of red blood cells and DNA, and also improves neurotransmitter function. Vegetarians and vegans may be at particular risk for vitamin B12 deficiency deficiency because plants don't generally produce it, although some algae, fermented plants, mushrooms and yeast products have some.
6- Folate:
Folate is a vitamin B that’s particularly important for women of childbearing age, which is why prenatal vitamins usually contain a hefty dose. Folate supports healthy growth and function and can reduce the risk of birth defects, particularly those involving the brain and spine.
7- Magnesium:
Magnesium helps support bone health and assists in energy production, and adults need between 310 and 420 mg, depending on sex and age. Although deficiency is fairly uncommon in otherwise healthy people, certain medications (including some antibiotics and diuretics) and health conditions (such as type 2 diabetes and Crohn’s disease) can limit the absorption of magnesium or increase the loss of this nutrient from the body.
- Treatment of Malnutrition:
- Undernutrition is treated with nutritional supplements. This might mean individual micronutrients, or it might mean refeeding with a custom, high-calorie nutritional formula designed to restore everything your body is missing. Severe undernutrition can take weeks of refeeding to correct. But refeeding can be dangerous, especially in the first few days. Your body changes in many ways to adapt to undernutrition. Refeeding asks it to change back to its old way of operating, and sometimes that change is more than it's prepared to handle. It’s best to begin refeeding under close medical observation to prevent and manage the complications of refeeding syndrome, which can be serious and even life-threatening.
- Overnutrition is generally treated with weight loss, diet and lifestyle changes. Losing extra weight can help reduce your risk of developing secondary conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. Weight loss treatment may include diet and exercise plans, medications or medical procedures. You may also need to treat an underlying condition, such as thyroid disease, or a mental health disorder.
- Weight loss can be rapid or it can be long and gradual, depending on the path you take. But after you lose weight, it’s the lifestyle changes you stick with that will help keep it off. This may involve long-term support systems such as counseling, behavioral therapy, support groups and education in nutrition.